What is Cloud Computing?
The basic definition of Cloud computing is on-demand computing.
Cloud computing is defined as a type of computing that relies on sharing computing resources rather than having local servers or personal devices to handle applications.
In this type of computing the shared resources are provided on demand. Which means cloud resources are not only shared by multiple users but can also be dynamically reallocated as per demand. Scaling up and down as per demand is a specialty of cloud computing.
The cloud concept is built on layers, each providing a distinct level of functionality. This stratification of the cloud's components has provided a means for the layers of cloud computing to becoming a commodity just like electricity, telephone service, or natural gas. The commodity that cloud computing sells is computing power at a lower cost and expense to the user. Cloud computing is poised to become the next mega-utility service.
From an organization point of view it is cost effective as the user (organization) has to pay only what they use and simultaneously they also get more resources easily when required. This is in contrast to the traditional CAPEX model where the organization invests in getting servers, space, maintenance initially and then gets a return over its investment over a period of time.
So when a company goes for cloud based computing they avoid upfront infrastructure cost and instead can focus on their core business.
Cloud computing is defined as a type of computing that relies on sharing computing resources rather than having local servers or personal devices to handle applications.
In this type of computing the shared resources are provided on demand. Which means cloud resources are not only shared by multiple users but can also be dynamically reallocated as per demand. Scaling up and down as per demand is a specialty of cloud computing.
The cloud concept is built on layers, each providing a distinct level of functionality. This stratification of the cloud's components has provided a means for the layers of cloud computing to becoming a commodity just like electricity, telephone service, or natural gas. The commodity that cloud computing sells is computing power at a lower cost and expense to the user. Cloud computing is poised to become the next mega-utility service.
From an organization point of view it is cost effective as the user (organization) has to pay only what they use and simultaneously they also get more resources easily when required. This is in contrast to the traditional CAPEX model where the organization invests in getting servers, space, maintenance initially and then gets a return over its investment over a period of time.
So when a company goes for cloud based computing they avoid upfront infrastructure cost and instead can focus on their core business.
Cloud computing shares characteristics with:
- Client–server model — Client–server computing refers broadly to any distributed application that distinguishes between service providers (servers) and service requestors (clients).
- Grid computing — "A form of distributed and parallel computing, whereby a 'super and virtual computer' is composed of a cluster of networked, loosely coupled computers acting in concert to perform very large tasks."
- Mainframe computer — Powerful computers used mainly by large organizations for critical applications, typically bulk data processing such as: census; industry and consumer statistics; police and secret intelligence services; enterprise resource planning; and financial transaction processing.
- Utility computing — The "packaging of computing resources, such as computation and storage, as a metered service similar to a traditional public utility, such as electricity."
- Peer-to-peer — A distributed architecture without the need for central coordination. Participants are both suppliers and consumers of resources (in contrast to the traditional client–server model).
Source: Wikipedia
Cloud Computing Model
The cloud computing model is comprised of a front end and a back end. These two elements are connected through a network, in
Virtualization
software makes it possible to run multiple operating systems and
multiple applications on the same server at the same time - See more at:
http://www.businessnewsdaily.com/5791-virtualization-vs-cloud-computing.html#sthash.ctPXC9eI.dpuf
most cases the Internet. The front end is the vehicle by which the user interacts with the system; the back end
is the cloud itself. The front end is composed of a client computer, or the computer network of an enterprise, and
the applications used to access the cloud. The back end provides the applications, computers, servers, and data
storage
that creates the cloud of services.What is the role of virtualization in Cloud Computing?
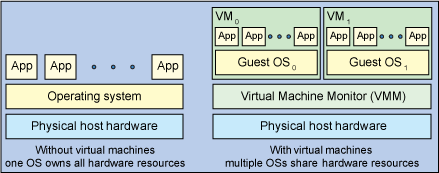
Virtualization is the fundamental technology that powers cloud computing. It separates physical infrastructures to create various dedicated resources. The software that is used to do this is called as Virtual Machine Monitor (VMM).Virtual Machine Monitor makes it possible to run multiple operating systems and multiple applications on the same server at the same time. From the user's point of view, the system is a self-contained computer which is isolated from other users. In reality, every user is being served by the same machine. A virtual machine is one operating system (OS) that is being managed by an underlying control program allowing it to appear to be multiple operating systems. In cloud computing, VMM allows users to monitor and thus manage aspects of the process such as data access, data storage, encryption, addressing, topology, and workload movement.
Source:IBM
How is cloud computing different than traditional Hosting?
The difference between cloud computing and traditional hosting is the implied scalability and separation of components. Cloud computing most often refers to running in a virtualized environment that automatically scales up or down based on demand. Additionally, cloud computing is used to refer to applications that are either themselves hosted in parts across multiple virtual hosts or utilize services provided by separate hosts or services.
What are the Layers provided by Cloud ?
Cloud provides three layers: Infrastructure, Platform and Application.- The infrastructure layer is the foundation of the cloud. It consists of the physical assets — servers, network devices, storage disks, etc. Infrastructure as a Service (IaaS) has providers such as the IBM® Cloud. Using IaaS you don’t actually control the underlying infrastructure, but you do have control of the operating systems, storage, deployment applications, and, to a limited degree, control over select networking components.
- The middle one is the platform layer. It provides the application infrastructure. Platform as a Service (PaaS) provides access to operating systems and associated services. It provides a way to deploy applications to the cloud using programming languages and tools supported by the provider. In the platform layer you do not have to manage or control the underlying infrastructure, but you do have control over the deployed applications and, to some degree over application hosting environment configurations.
- The top layer is the application layer, the layer most visualize as the cloud. Applications run here and are provided on demand to users. Software as a Service (SaaS) has providers such as Google Pack. Google Pack includes Internet accessible applications, tools such as Calendar, Gmail, Google Talk, Docs, and many more.
Source:IBM
What is IAAS, PAAS and SAAS?
Cloud computing adopts concepts from Service-oriented Architecture (SOA) that can help the user break these problems into services that can be integrated to provide a solution. Cloud computing provides all of its resources as services, and makes use of the well-established standards and best practices gained in the domain of SOA to allow global and easy access to cloud services in a standardized way.These services can be divided into, IAAS (Infrastructure as a service), PAAS (Platform as a service) and SAAS (Software as a service). These are also called as Cloud Service Models.
Cloud-computing providers offer their "services" as per the above models.
Cloud Formation or Cloud Deployment Models
There are four types of cloud deployment models/formations : private (on premise), public, hybrid and community.
- Public clouds are available to the general public or a large industry group and are owned and provisioned by an organization selling cloud services. A public cloud is what is thought of as the cloud in the usual sense; that is, resources dynamically provisioned over the Internet using web applications from an off-site third-party provider that supplies shared resources and bills on a utility computing basis.
- Private clouds exist within your company's firewall and are managed by your organization. They are cloud services you create and control within your enterprise. Private clouds offer many of the same benefits as the public clouds — the major distinction being that your organization is in charge of setting up and maintaining the cloud.
- Hybrid clouds are a combination of the public and the private cloud using services that are in both the public and private space. Management responsibilities are divided between the public cloud provider and the business itself. Using a hybrid cloud, organizations can determine the objectives and requirements of the services to be created and obtain them based on the most suitable alternative.
- Community clouds are the ones which are created to serve a common function or purpose. Basically it is suitable for a group of organizations which serves a common mission, policies, security, regulatory compliance needs and so on.
virtualization
is software that separates physical infrastructures to create various
dedicated resources. It is the fundamental technology that powers cloud
computing - See more at:
http://www.businessnewsdaily.com/5791-virtualization-vs-cloud-computing.html#sthash.ctPXC9eI.dpuf
virtualization
is software that separates physical infrastructures to create various
dedicated resources. It is the fundamental technology that powers cloud
computing - See more at:
http://www.businessnewsdaily.com/5791-virtualization-vs-cloud-computing.html#sthash.ctPXC9eI.dpuf
virtualization
is software that separates physical infrastructures to create various
dedicated resources. It is the fundamental technology that powers cloud
computing - See more at:
http://www.businessnewsdaily.com/5791-virtualization-vs-cloud-computing.html#sthash.ctPXC9eI.dpuf
virtualization
is software that separates physical infrastructures to create various
dedicated resources. It is the fundamental technology that powers cloud
computing - See more at:
http://www.businessnewsdaily.com/5791-virtualization-vs-cloud-computing.html#sthash.ctPXC9eI.dpuf